by BehindJava
What is a Bubble Sort & How does it work
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about bubble sort and its implementation in detail.
Bubble Sort
- In-place algorithm.
- O(n^2) time complexity - Quadratic.
- It will take 100 steps to sort 10 items, 10000 steps to sort 100 items and 1000000 steps to sort 1000 items.
- Algorithm’s performance degrades quickly as the number of items you need to sort grows, but it’s a commonly taught algorithm.
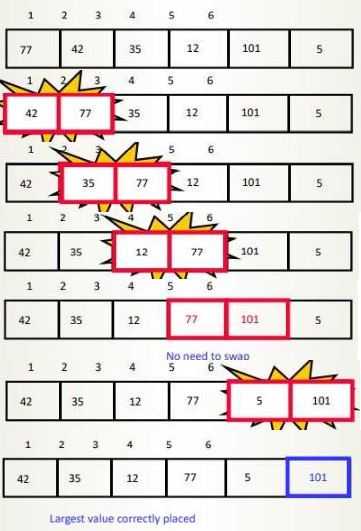
“Bubbling Up” the Largest Element
-
Traverse a collection of elements.
- Move from the front to the end
- “Bubble” the largest value to the end using pair-wise comparisons and swapping.
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Bubble (DATA, N)
- Repeat Step 2 and 3 for K=1 to N-1.
- [Initialize Pass Pointer P] Set P=1.
-
[Execute Pass] Repeat while P <= N-K.
- if DATA [P] > DATA [P+1], then:
Swap DATA [P] and DATA[P+1]
[End of if Structure.] - Set P = P+1.
[End of Inner Loop.]
[End of Step1 Outer Loop.]
- if DATA [P] > DATA [P+1], then:
- Exit
Bubble Sort Programmatic Implementation in Java
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intArray = { 77, 42, 35, 12, 101, 5 };
for (int lastUnsortedIndex = intArray.length - 1; lastUnsortedIndex > 0;
lastUnsortedIndex--) {
for (int i = 0; i < lastUnsortedIndex; i++) {
if (intArray[i] > intArray[i + 1]) {
swap(intArray, i, i + 1);
}}}
for (int i = 0; i < intArray.length; i++) {
System.out.print(intArray[i] + " ");
}}
public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) {
return;
}
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}}Output:
5 12 35 42 77 101