by BehindJava
Data Structures - Radix Sort Algorithm
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about radix sort in detail and its algorithmic implementation.
Radix Sort
- Counting sort is often used as the sort algorithm for radix sort - must be stable counting sort.
- O(n) - can achieve this because we’re making assumptions about the data we’re sorting.
- Even so, it often runs slower than O(n log n) algorithms because of the overhead involved.
- In-place depends on which sort algorithm you use.
- Stable algorithm.
- Makes assumptions about the data.
- Data must have same radix and width.
- Because of this, data must be integers or strings.
- Sort based on each individual digit or letter position.
- Start at the rightmost position.
- Must se a stable sort algorithm at each stage.
Radix Algorithm
- radixSort(arr)
- max = largest element in the given array
- d = number of digits in the largest element (or, max). Now, create d buckets of size 0 - 9
- for i -> 0 to d.
sort the array elements using counting sort (or any stable sort) according to the digits at
the ith place.
Radix Sort Programmatic Implementation in Java
public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
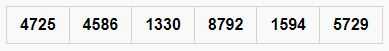
int[] radixArray = { 4725, 4586, 1330, 8792, 1594, 5729 };
radixSort(radixArray, 10, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < radixArray.length; i++) {
System.out.print(radixArray[i]+ " ");
}
}
public static void radixSort(int[] input, int radix, int width) {
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
radixSingleSort(input, i, radix);
}
}
public static void radixSingleSort(int[] input, int position, int radix) {
int numItems = input.length;
int[] countArray = new int[radix];
for (int value : input) {
countArray[getDigit(position, value, radix)]++;
}
// Adjust the count array
for (int j = 1; j < radix; j++) {
countArray[j] += countArray[j - 1];
}
int[] temp = new int[numItems];
for (int tempIndex = numItems - 1; tempIndex >= 0; tempIndex--) {
temp[--countArray[getDigit(position, input[tempIndex], radix)]] = input[tempIndex];
}
for (int tempIndex = 0; tempIndex < numItems; tempIndex++) {
input[tempIndex] = temp[tempIndex];
}
}
public static int getDigit(int position, int value, int radix) {
return value / (int) Math.pow(radix, position) % radix;
}
}Output:
1330 1594 4586 4725 5729 8792