by BehindJava
What is a Stack in Data Structures
In this blog, we are going to learn about stack and its implementation with a detailed example.
Stack
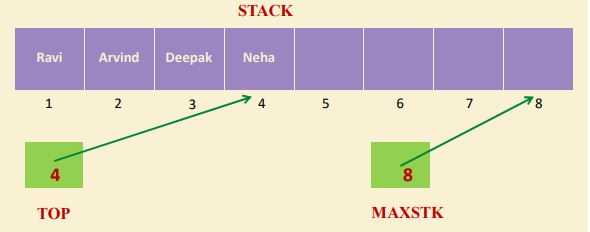
- A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the “TOP” of the Stack.
- Stack is a LIFO (Last In First Out) data structure.
- Elements are removed from a stack in the reverse order of that in which they were inserted into the stack.
- Stack is an Abstract Data Type.
Stack Operations
- LIFO - Last in, First out.
- PUSH - Adds an item as the top item on the stack.
- POP - Removes the top item on the stack.
- PEEK - Gets the top item on the stack without popping it.
Examples: Stack of Dishes, Stack of Books, packet of Biscuit etc.
Note: AVAIL List is also implemented using STACK.
Stack Time Complexity
- O(1) for push, pop and peek, when using a linked list.
- If you use any array then push is O(n), because the array may have to be resized.
- If you know the maximum number of items that are on the stack, an array could be a good choice.
- If memory has limitations array is a good choice.
- Linked List is Ideal.
import java.util.Stack;
public class BehindJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<>();
stk.push(10);
stk.push(9);
stk.push(8);
stk.push(7);
stk.push(6);
stk.push(5);
System.out.println(stk);
stk.pop();
System.out.println(stk);
stk.peek();
System.out.println(stk);
System.out.println(stk.peek());
}
}Output:
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5]
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6]
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6]
6