What is Web 3.0 Blockchain, Its building blocks, and Evolution of the Internet
In this tutorial, we are going to understand Web 3.0 in detail. First things first, we will see the evolutionary process of the web architecture 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0.
Evolution of the Internet
Web 1.0
Back then, we have a web page rendered on a browser that was connected to the backend servers which is just retrieving the information and this information is just retrieved and we had read-only access to the information.
For example Wikipedia, Britannica encyclopedia used to give information. so people used to go to the internet just to go and look up what is present inside few websites like listed above. Let us take an example, Britannica encyclopedia is used to be the central hub for searching the information, understanding, and learning the information. So this is all about Web 1.0 where we had read-only information on the web pages on the internet.
Web 2.0
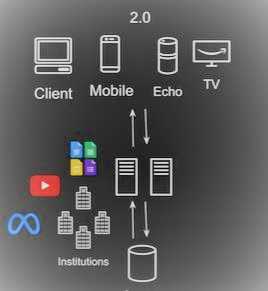
Web 2.0 is much evolved compared to the web 1.0 where we had both read and write facilities for which we had multiple devices in the current day trend for example we have browsers, mobile applications, tv’s that are connected to a backend system or API and these API’s interact with the backend where we have all these stored and gets processed based on the requirement.
A classic example for Web 2.0 would be Wikipedia where you as a user can go and modify it, unlike Britannica encyclopedia where only the Britannica encyclopedia team is responsible for the updates. Since they are the only ones who have access to manage the website. But in the case of Wikipedia as a user, you can edit the information which enables both read and write capabilities.
Also inside the Web 2.0 space, we do have applications like MS office web-based, youtube, facebook’s meta, etc which are managed by the individual organizations like, youtube is managed by Google, and meta is managed by Facebook, and etc.
This is how Web 2.0 stack looks like and if you need to connect to any web application that is hosted on the internet, you need to have it hosted on a central entity that will manage the infrastructure of the website and we have a way to modify and edit information and also read information from the website.
All the current day devices which we use fall under Web 2.0.
Web 3.0
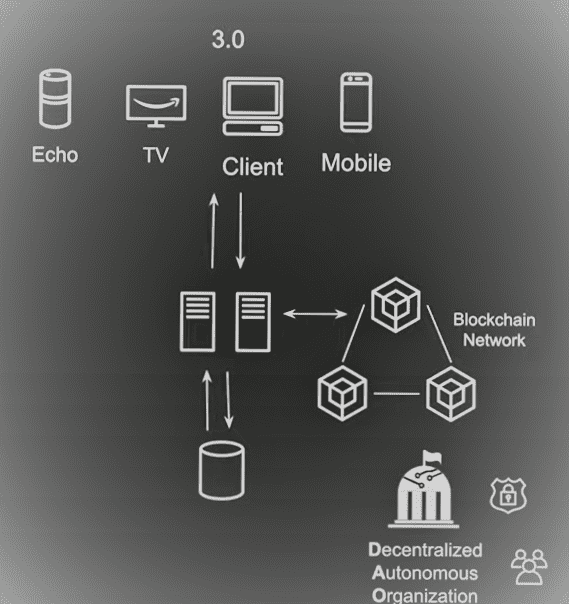
Web 3.0 is going to be the evolutionary change in the internet and we have similar devices from Web 2.0 available in Web 3.0 along with the integration with devices like AR and VR i.e., Augmented reality and Virtual reality. Facebook is launching something called metaverse and these are the few clients that are going to connect to the internet and we also have the backend servers which is going to be exposed via API’s or UI’s etc.
They will interact with a different blockchain network which is interconnected and these blockchains are managed by the decentralized organizations or decentralized autonomous organizations and these organizations are composed of people or a group of institutions, which form a particular blockchain network.
By adding more users to it or may reduce the number of users or make the users to a minimal, and then make them secure by controlling the whole application and its ecosystem within this particular network.
For example, you might host a website called behindjava.com where we can post tutorials. Now, behindjava.com is managed by me and a few other individual community members, and the whole website is managed by the community-driven approach.
So this is completely decentralized. So it won’t be stored and all the decision making will be shared across the parties within that particular network or organization and even if I decide to take something down I cannot do that without the majority of the participants agreeing for a particular feature or change. Now that’s how the whole decentralized autonomous organizations are going to function and without multiple parties concern and majority stake you cannot change something within that network.
To differentiate Web 3.0 and Web 2.0 there’s is one more deciding factor which is called Tokenization. Cryptocurrencies are very popular these days and these are the outcome of the blockchain network.
For example, there is a platform called OTC which is built using a blockchain network. In this, there is cryptocurrency LBRY Credits used to monetize the creators and also the viewers. So the main differentiation between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 is this. When you use Web 2.0 you don’t have a way to earn money out of it, unless and until it is provided as a service.
To understand this better. When you watch a youtube ad, you don’t get paid for it instead only creators get paid. But in Web 3.0 both viewers and creators get paid and also the people in the network get paid for it.
Web 3.0 Architecture
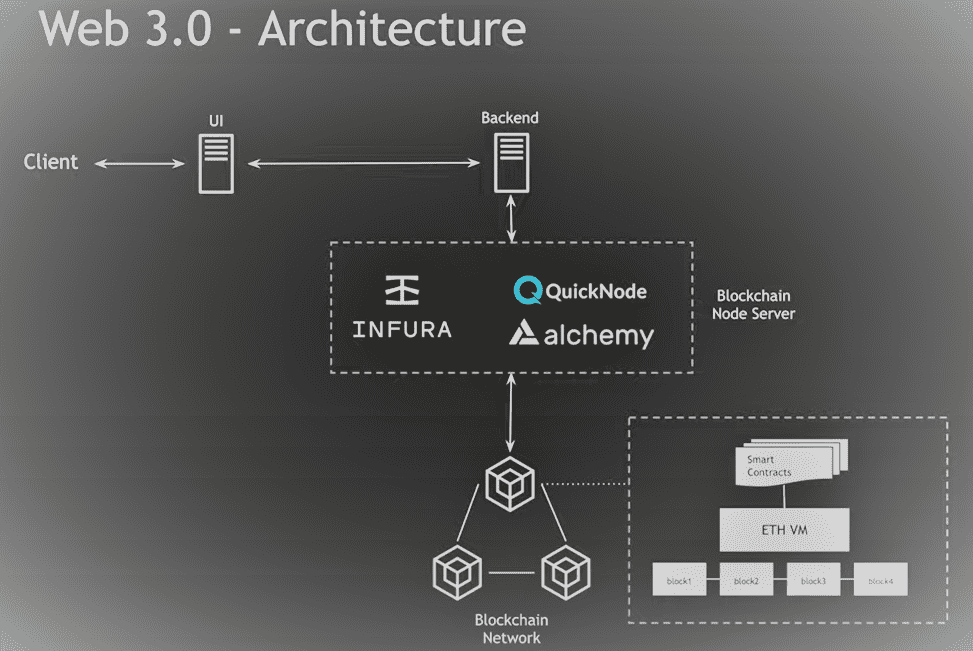
Let’s look deeper into the Web 3.0 architecture within the blockchain and how applications are going to interact with the blockchain network.
Let’s take an example of a client, browser, or web app that interacts with the UI application and UI to the backend where it is a standard flow in every case.
Now the backend servers or application is going to connect with the blockchain network, and these blockchain networks are interconnected. Between the backend server and blockchain network, we need to have an intermediary node server using which you can be connected with the blockchain network. There are different third party applications available in the market like Infura, QuickNode, Alchemy, etc. which provide API’s to interact with the Ethereum(Ethereum is one implementation of the blockchain which is similar to bitcoin) based blockchain.
Now inside the blockchain network, we will have an Ethereum virtual machine similar to a Java virtual machine on which we can run smart contracts or business logic’s under which we have the blockchain technology where the blocks are connected in terms of transactions with the ledger mechanism.
Summary:
The evolution of the internet in terms of Web 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and Web 3.0 is getting built and Ethereum is building Web 3.0 using which you can create and deploy applications and have them controlled in a decentralized form.